Trilinos - Nonlinear (02-trilinos-nonlinear)¶
This example is analogous to the previous one, but the underlying problem is nonlinear and thus NOX will do more than one nonlinear iteration. First we use the Newton’s method in Hermes (assembling via the DiscreteProblem class and matrix problem solution via UMFpack). Second, assembling is done using the DiscreteProblem class in Hermes and the discrete problem is solved using the Trilinos NOX solver (using Newton’s method or JFNK, with or without preconditioning).
Model problem¶
This example is concerned with the nonlinear equation
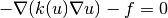
where
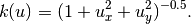
Boundary conditions are zero Dirichlet.
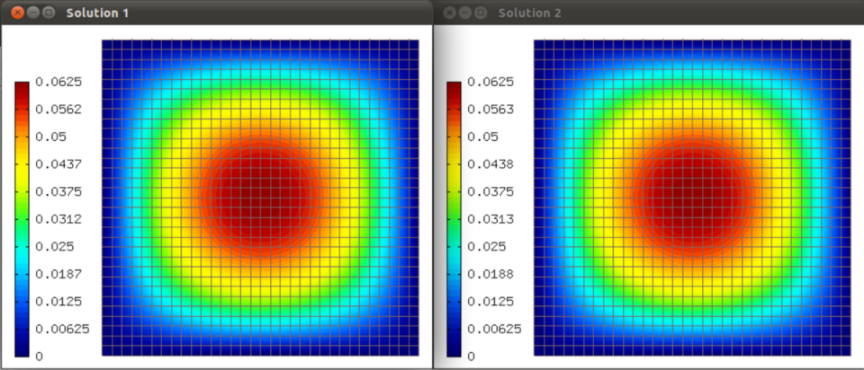
Manufactured exact solution¶
We have manufactured an exact solution has the form
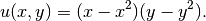
Again let is skip the UMFpack part and go directly to NOX:
Calculating initial condition for NOX¶
The initial coefficient vector can be either set to zero, or orthogonal projection can be used as in the previous example:
// Project the initial condition on the FE space to obtain initial
// coefficient vector for the Newton's method.
double* coeff_vec = new double[ndof];
// We can start with a zero vector.
memset(coeff_vec, 0, ndof * sizeof(double));
// Or we can project the initial condition to obtain the initial coefficient vector.
//info("Projecting to obtain initial vector for the Newton's method.");
//CustomInitialSolution sln_tmp(&mesh);
//OGProjection<double> ogProjection; ogProjection.project_global(&space, &sln_tmp, coeff_vec);
Initializing NOX¶
// Initialize the NOX solver with the vector "coeff_vec".
info("Initializing NOX.");
NewtonSolverNOX<double> nox_solver(&dp2, message_type, "GMRES", "Newton", ls_tolerance, "", flag_absresid, abs_resid,
flag_relresid, rel_resid, max_iters);
nox_solver.set_init_sln(coeff_vec);
Setting a preconditioner¶
// Choose preconditioning.
RCP<Precond> pc = rcp(new MlPrecond("sa"));
if (PRECOND)
{
if (JFNK) nox_solver.set_precond(pc);
else nox_solver.set_precond("ML");
}
Calling NOX¶
// Solve the nonlinear problem using NOX.
info("Assembling by DiscreteProblem, solving by NOX.");
Solution sln2;
if (nox_solver.solve())
{
Solution::vector_to_solution(nox_solver.get_solution(), &space, &sln2);
info("Number of nonlin iterations: %d (norm of residual: %g)",
nox_solver.get_num_iters(), nox_solver.get_residual());
info("Total number of iterations in linsolver: %d (achieved tolerance in the last step: %g)",
nox_solver.get_num_lin_iters(), nox_solver.get_achieved_tol());
}
else
error("NOX failed.");