Nonlinear Example (03-nonlinear)¶
Model problem¶
Showing a nonlinear time-dependent problem is not really necessary since linear and nonlinear problems are treated in the same way. But let us show one anyway. Our model problem will be a time-dependent version of the example used in part P02:
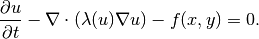
We prescribe nonhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions
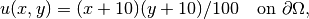
and the same function is used to define the initial condition. The
problem will be solved in the square 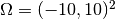 and time interval
and time interval 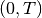 .
.
Weak formulation¶
In order to use arbitrary Runge-Kutta methods, the time derivative is put on the left-hand side of the equation and everything else is put on the right:
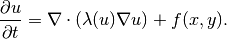
Then the time derivative term is skipped and we write the weak form for the stationary residual (right-hand side) only:
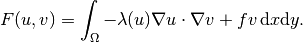
Weak forms¶
After inverting the sign of the custom nonlinearity,
double CustomNonlinearity::value(double u) const
{
return -1 - Hermes::pow(u, alpha);
}
the DefaultWeakFormPoisson can be used:
// Initialize the weak formulation
CustomNonlinearity lambda(alpha);
Hermes2DFunction<double> f(heat_src);
DefaultWeakFormPoisson<double> wf(HERMES_ANY, &lambda, &f);
Time stepping loop¶
The time stepping loop is analogous to the previous example:
// Time stepping loop:
double current_time = 0; int ts = 1;
do
{
// Perform one Runge-Kutta time step according to the selected Butcher's table.
info("Runge-Kutta time step (t = %g s, tau = %g s, stages: %d).",
current_time, time_step, bt.get_size());
runge_kutta.set_newton_tol(NEWTON_TOL);
runge_kutta.set_newton_max_iter(NEWTON_MAX_ITER);
runge_kutta.set_verbose_output(true);
runge_kutta.set_newton_damping_coeff(1.0);
runge_kutta.set_newton_max_allowed_residual_norm(1e10);
Hermes::vector<Solution<double>*> slns_time_prev;
slns_time_prev.push_back(&sln_time_prev);
Hermes::vector<Solution<double>*> slns_time_new;
slns_time_new.push_back(&sln_time_new);
runge_kutta.setTime(current_time);
runge_kutta.setTimeStep(time_step);
try
{
runge_kutta.rk_time_step_newton(slns_time_prev, slns_time_new);
}
catch(Exceptions::Exception& e)
{
std::cout << e.what();
}
// Update time.
current_time += time_step;
// Show the new time level solution.
char title[100];
sprintf(title, "Solution, t = %g", current_time);
sview.set_title(title);
sview.show(&sln_time_new);
oview.show(&space);
// Copy solution for the new time step.
sln_time_prev.copy(&sln_time_new);
// Increase counter of time steps.
ts++;
}
while (current_time < T_FINAL);