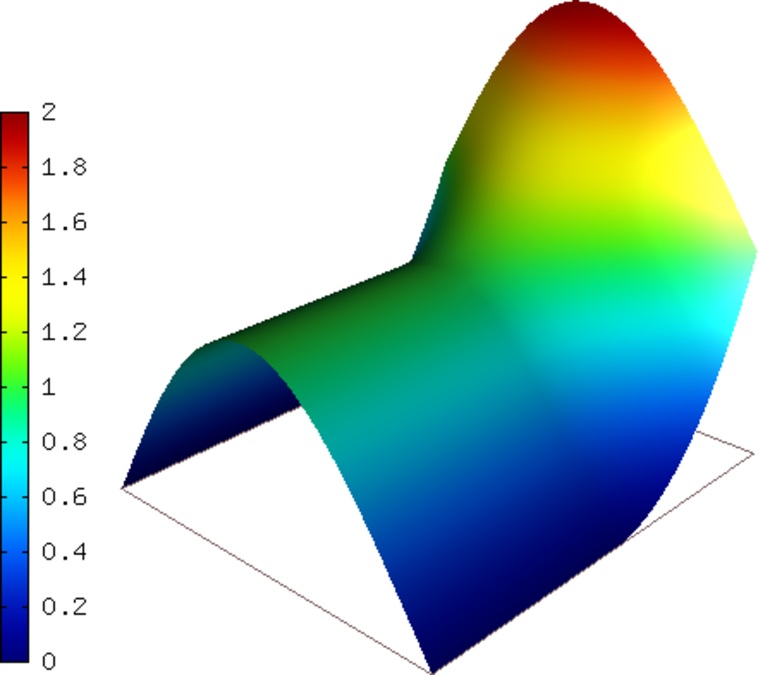
NIST-10 (Interior Line Singularity)¶
This example is an extension of Boundary Line Singularity (NIST-07) with an anisotropic solution to allow for a sloped line so that the singularity does not necessarily coincide with element edges.
Model problem¶
Equation solved: Poisson equation
(1)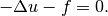
Domain of interest: 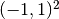 .
.
Boundary conditions: Dirichlet, given by exact solution.
Right-hand side¶
Obtained by inserting the exact solution into the equation.
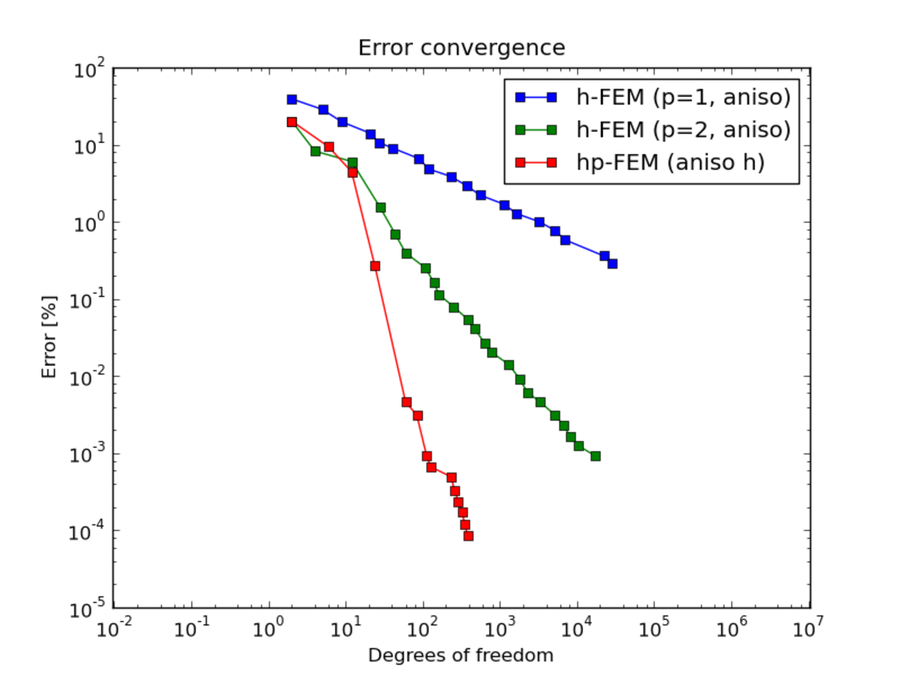
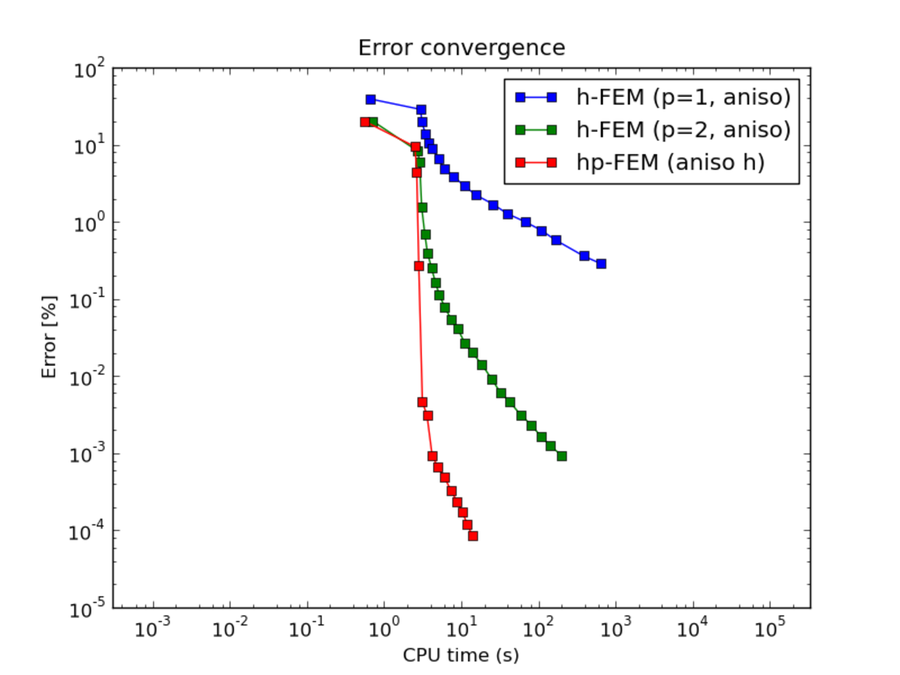
Comparison of h-FEM (p=1), h-FEM (p=2) and hp-FEM with anisotropic refinements¶
Final mesh (h-FEM, p=1, anisotropic refinements):
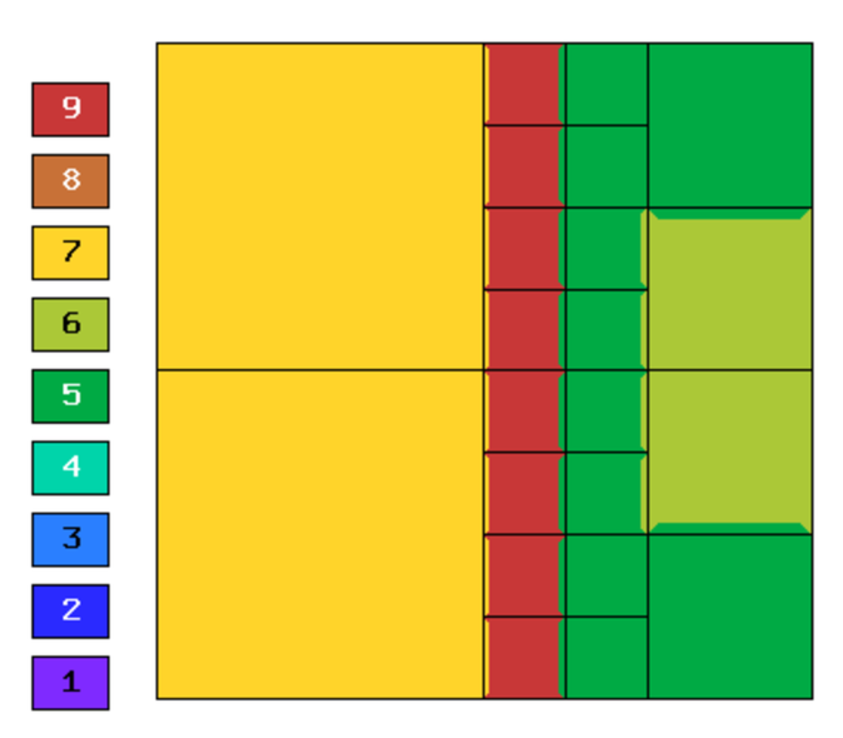
Final mesh (h-FEM, p=2, anisotropic refinements):
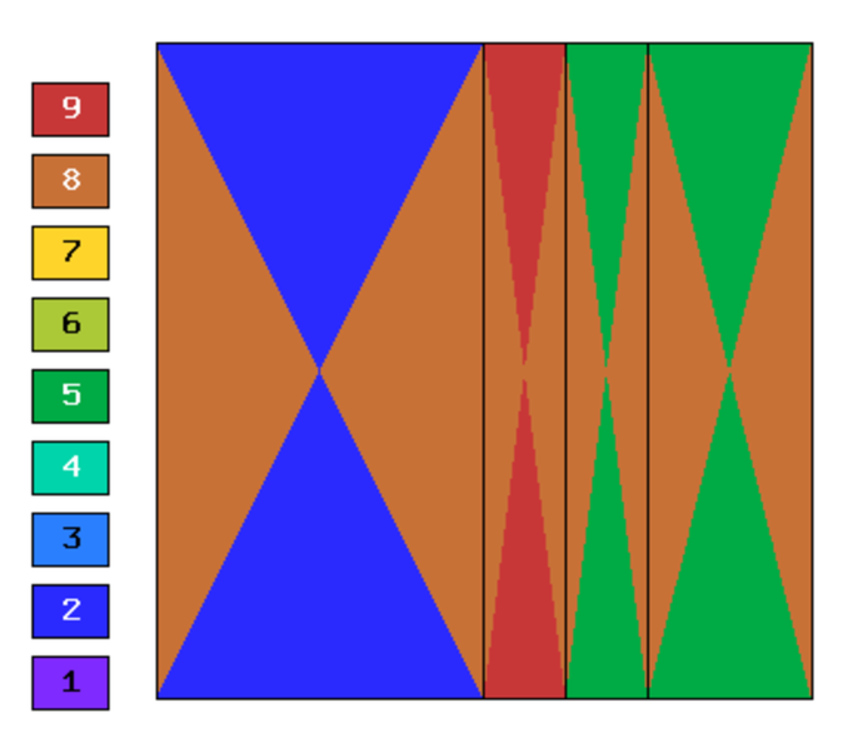
Final mesh (hp-FEM, h-anisotropic refinements):
DOF convergence graphs:
CPU convergence graphs:
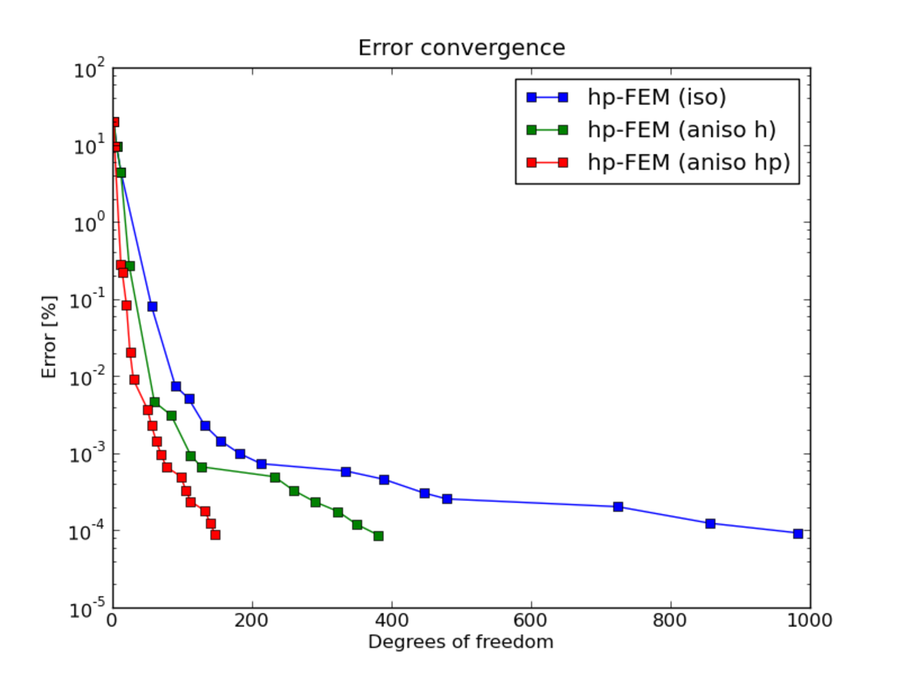
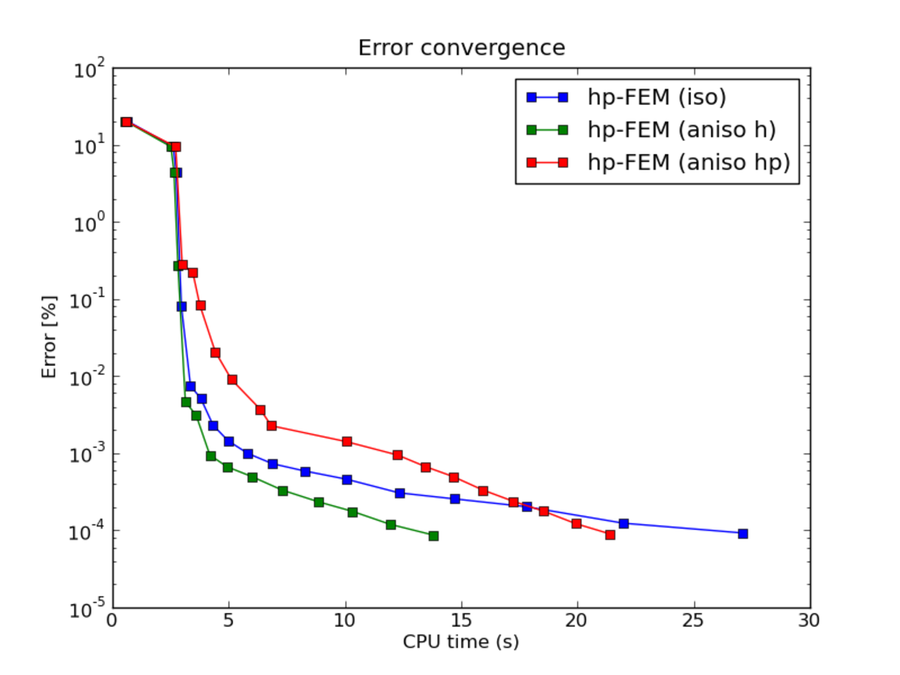
hp-FEM with iso, h-aniso and hp-aniso refinements¶
Final mesh (hp-FEM, isotropic refinements):
Final mesh (hp-FEM, h-anisotropic refinements):
Final mesh (hp-FEM, hp-anisotropic refinements):
DOF convergence graphs:
CPU convergence graphs:
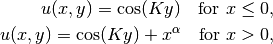
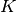 and
and 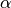 are real constants.
are real constants.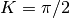 and
and 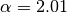 :
: