Space H(div) (04-space-hdiv)¶
The space H(div) in 2D is very similar in nature to the space H(curl), except its functions behave like (vector-valued) divergences of H1 functions. Finite element basis functions in the space H(div) are discontinuous across element interfaces but their normal components are continuous. The following code shows how to set up an H(div) space and visualize its basis functions:
int INIT_REF_NUM = 2; // Initial uniform mesh refinement.
int P_INIT = 3; // Polynomial degree of mesh elements.
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Load the mesh.
Mesh mesh;
MeshReaderH2D mloader;
mloader.load("square.mesh", &mesh);
// Initial mesh refinement.
for (int i = 0; i < INIT_REF_NUM; i++) mesh.refine_all_elements();
// Create an Hdiv space with default shapeset.
// (BC types and essential BC values not relevant.)
HdivSpace<double> space(&mesh, P_INIT);
// Visualise the FE basis.
VectorBaseView<double> bview("VectorBaseView", new WinGeom(0, 0, 700, 600));
bview.show(&space);
// Wait for all views to be closed.
View::wait();
return 0;
}
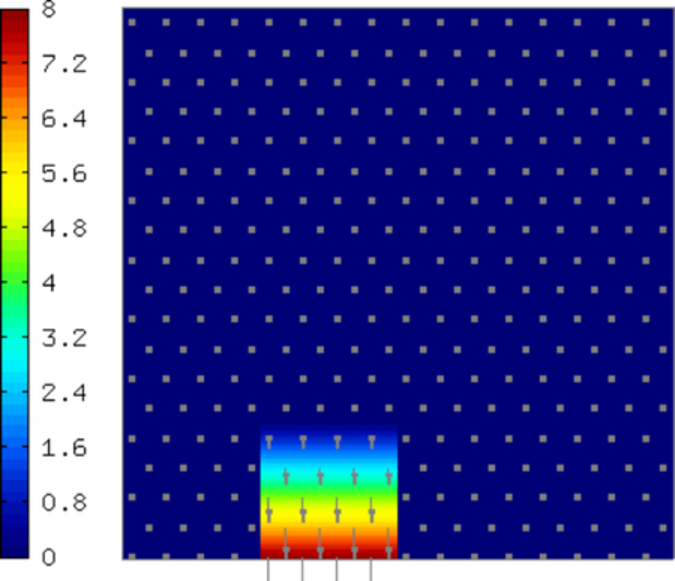
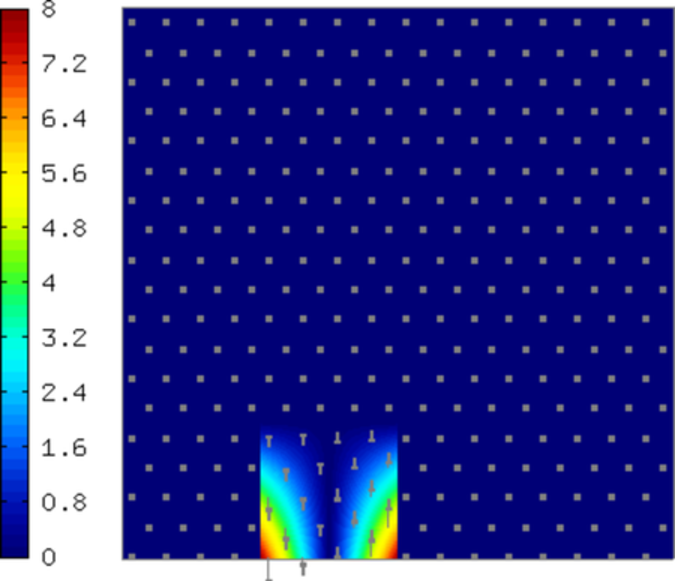
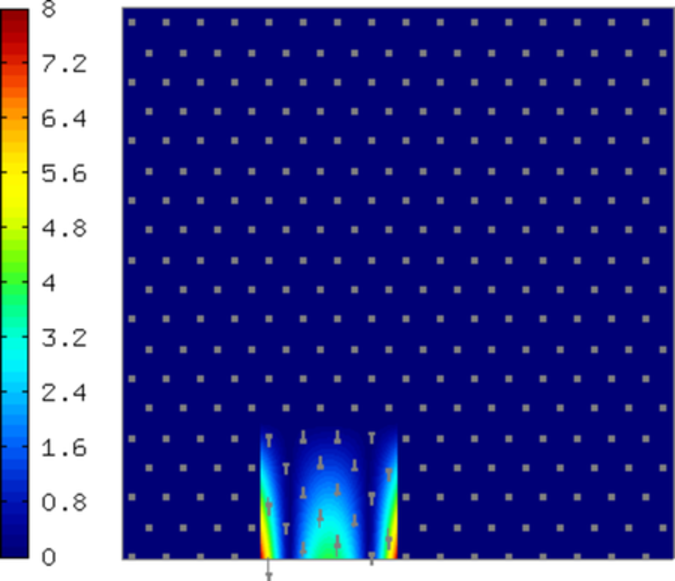
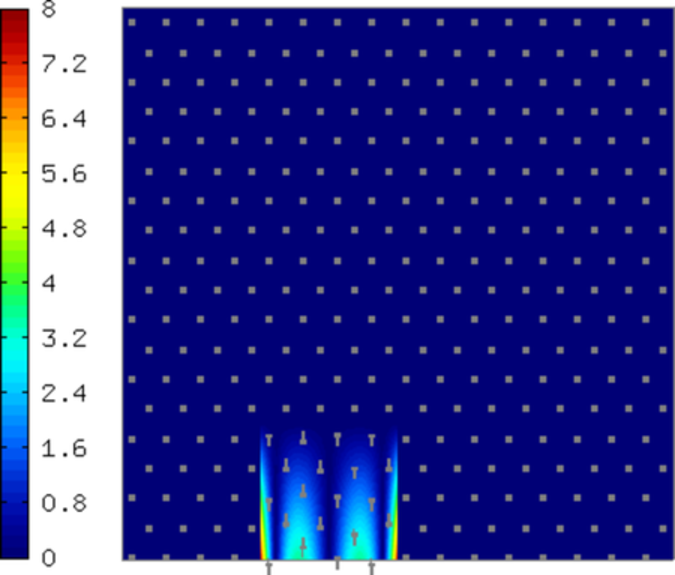
Sample edge functions of polynomial degrees 1, 2, 3, and 4 corresponding to a boundary edge are shown below:
So far the space H(div) only can be used with quadrilateral elements.