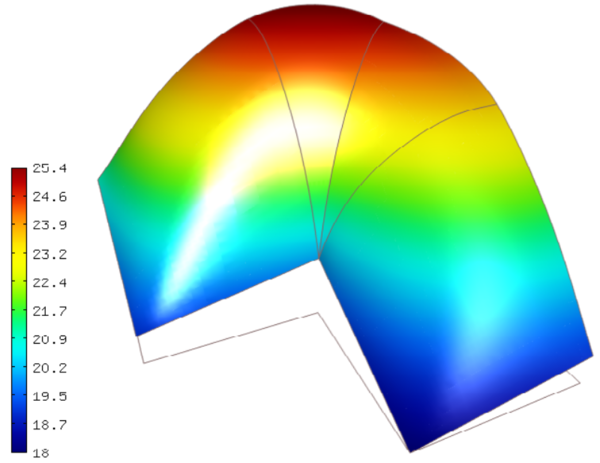
Neumann BC (05-bc-neumann)¶
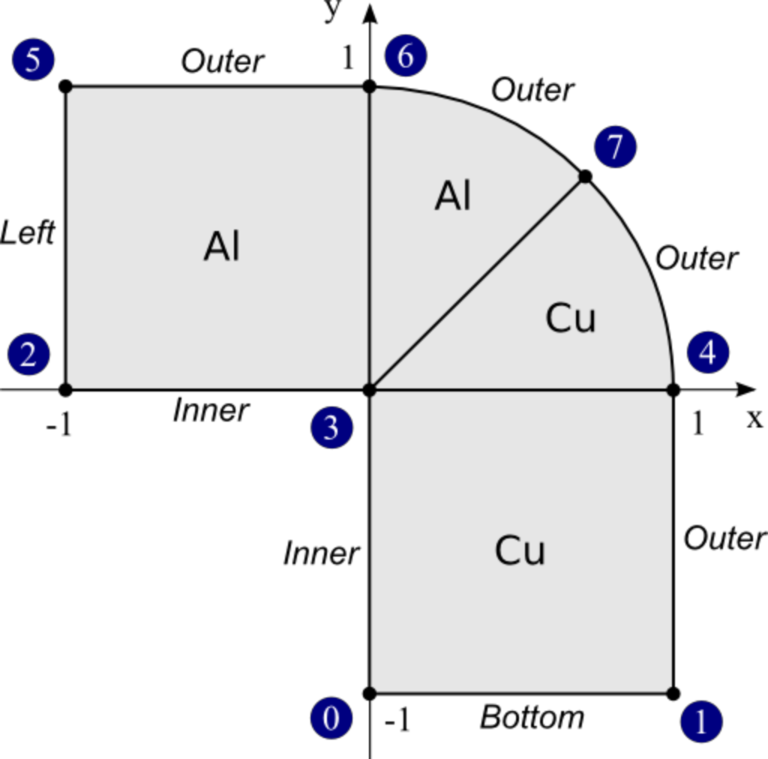
Let us recall the domain and boundary markers from the previous example:
We will solve the same equation
(1)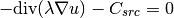
but now it will be equipped with a Neumann (heat flux) boundary condition
(2)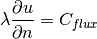
on the “Outer” boundary. Here 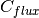 is a constant prescribed heat flux value.
Recall that
is a constant prescribed heat flux value.
Recall that 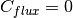 means a perfectly insulated (adiabatic) wall.
means a perfectly insulated (adiabatic) wall.
On the boundary parts “Bottom”, “Left” and “Inner” we keep the nonconstant Dirichlet condition from example P01/04-bc-dirichlet:
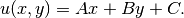
Since the solution on the “Outer” boundary is unknown, the test functions are nonzero there, and thus the weak formulation is
(3)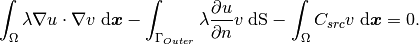
Using the Neumann condition (2), we obtain
(4)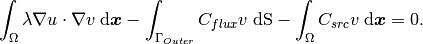
This weak formulation contains all integrals from the example 04-bc-dirichlet plus one new surface integral
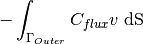
Using a default surface vector form¶
This integral can be added using the default H1-form DefaultVectorFormSurf. The header of the custom form CustomWeakFormPoissonNeumann is defined in definitions.h:
class CustomWeakFormPoissonNeumann : public WeakForm<double>
{
public:
CustomWeakFormPoissonNeumann(std::string mat_al, Hermes1DFunction<double>* lambda_al,
std::string mat_cu, Hermes1DFunction<double>* lambda_cu,
Hermes2DFunction<double>* vol_src_term, std::string bdy_heat_flux,
Hermes2DFunction<double>* surf_src_term);
};
and its constructor in definitions.cpp:
CustomWeakFormPoissonNeumann::CustomWeakFormPoissonNeumann(std::string mat_al, Hermes1DFunction<double>* lambda_al,
std::string mat_cu, Hermes1DFunction<double>* lambda_cu,
Hermes2DFunction<double>* vol_src_term, std::string bdy_heat_flux,
Hermes2DFunction<double>* surf_src_term) : WeakForm<double>(1)
{
// Jacobian forms - volumetric.
add_matrix_form(new DefaultJacobianDiffusion<double>(0, 0, mat_al, lambda_al));
add_matrix_form(new DefaultJacobianDiffusion<double>(0, 0, mat_cu, lambda_cu));
// Residual forms - volumetric.
add_vector_form(new DefaultResidualDiffusion<double>(0, mat_al, lambda_al));
add_vector_form(new DefaultResidualDiffusion<double>(0, mat_cu, lambda_cu));
add_vector_form(new DefaultVectorFormVol<double>(0, HERMES_ANY, vol_src_term));
// Residual forms - surface.
add_vector_form_surf(new DefaultVectorFormSurf<double>(0, bdy_heat_flux, surf_src_term));
};
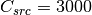 ,
, 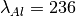 ,
, 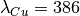 ,
,
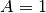 ,
, 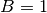 ,
, 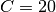 and
and