Saphir¶
Problem description¶
This is a standard nuclear engineering benchmark (IAEA number EIR-2) describing an external-force-driven configuration without fissile materials present, using one-group neutron diffusion approximation
(1)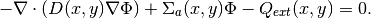
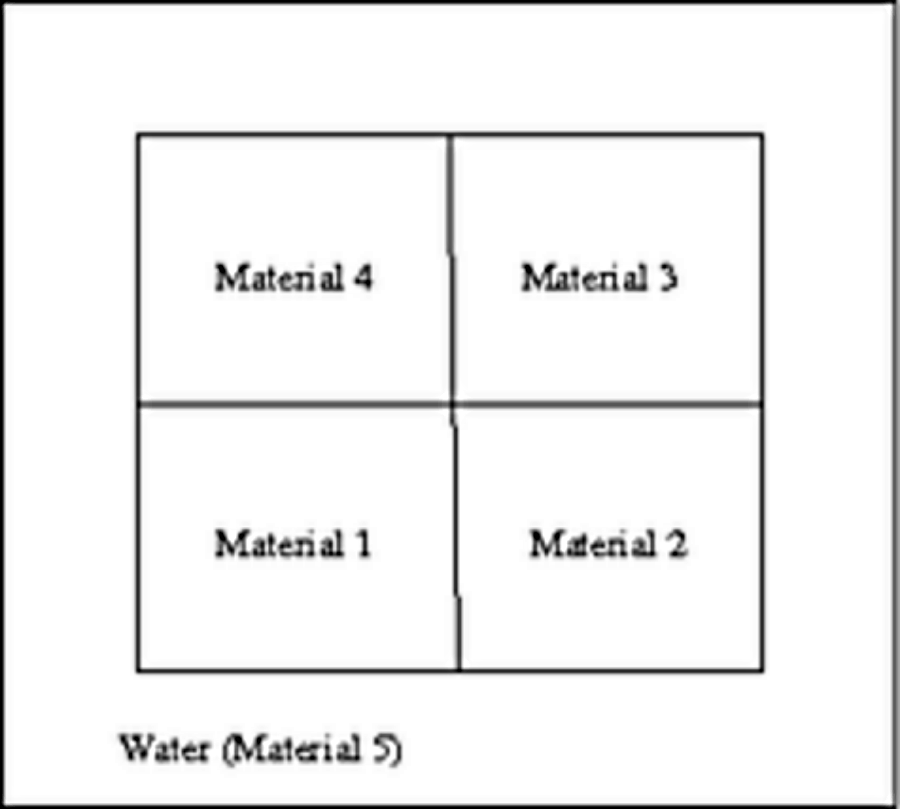
The domain of interest is a 96 x 86 cm rectangle consisting of five regions:
The unknown is the neutron flux 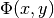 . The values of the diffusion coefficient
. The values of the diffusion coefficient
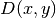 , absorption cross-section
, absorption cross-section 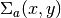 and the source term
and the source term 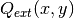 are constant in the subdomains. The source
are constant in the subdomains. The source 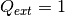 in areas 1 and 3 and zero
elsewhere. Boundary conditions for the flux
in areas 1 and 3 and zero
elsewhere. Boundary conditions for the flux 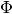 are zero everywhere.
are zero everywhere.
This example uses multiple weak forms that are associated with different material markers.
Sample results¶
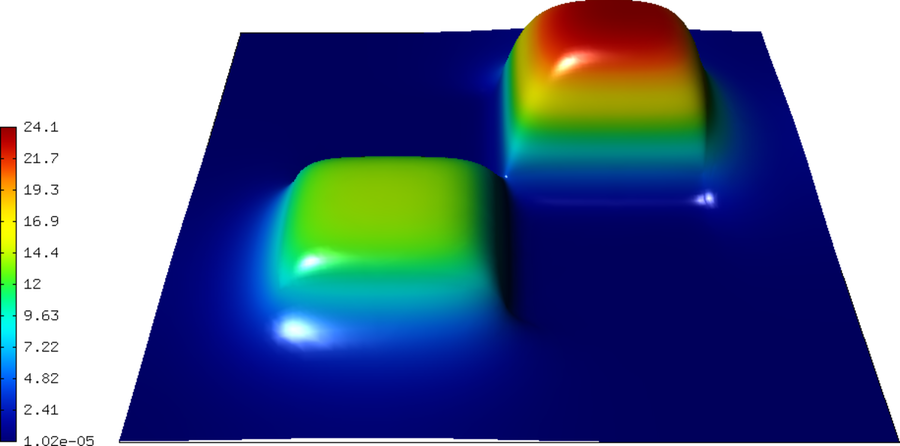
Solution:
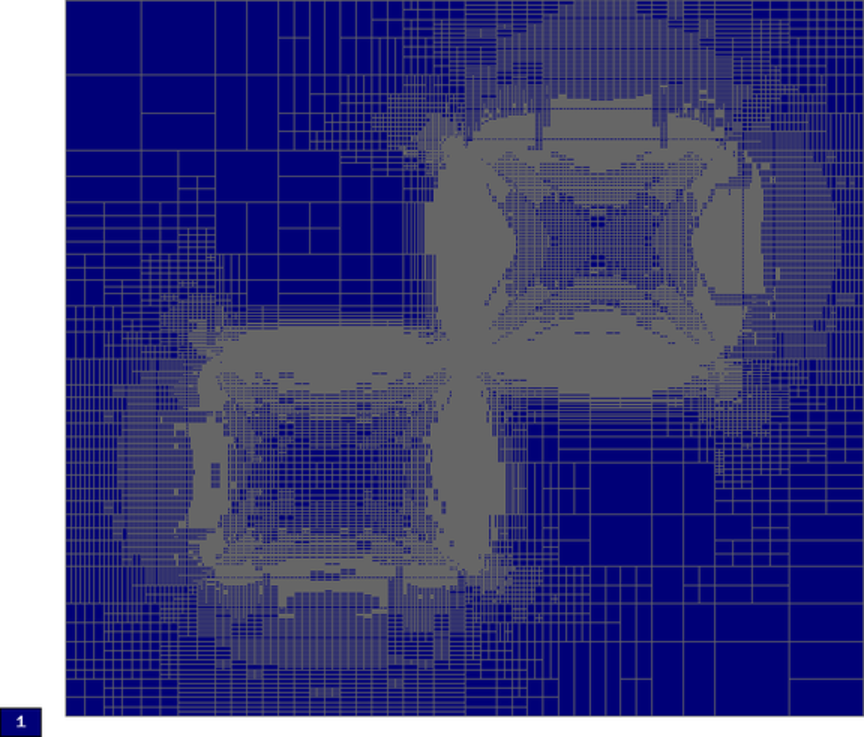
Final mesh (h-FEM with linear elements):
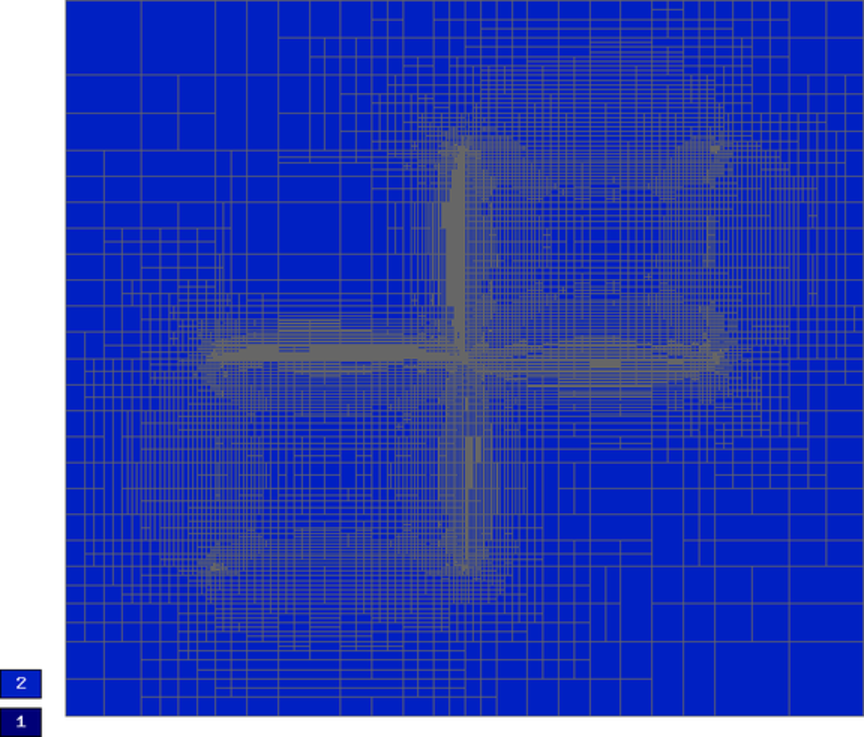
Final mesh (h-FEM with quadratic elements):
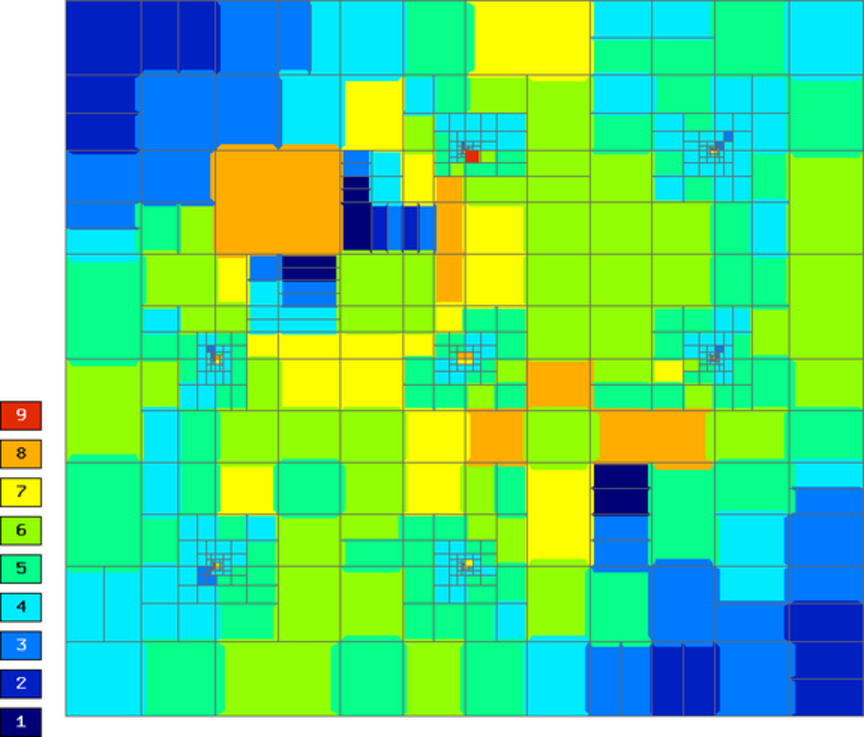
Final mesh (hp-FEM):
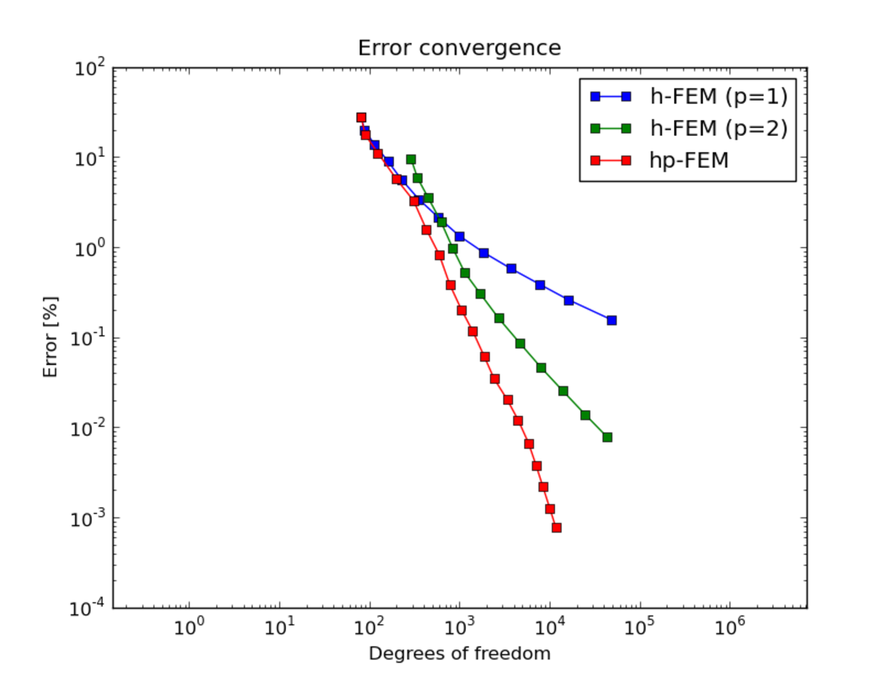
DOF convergence graphs:
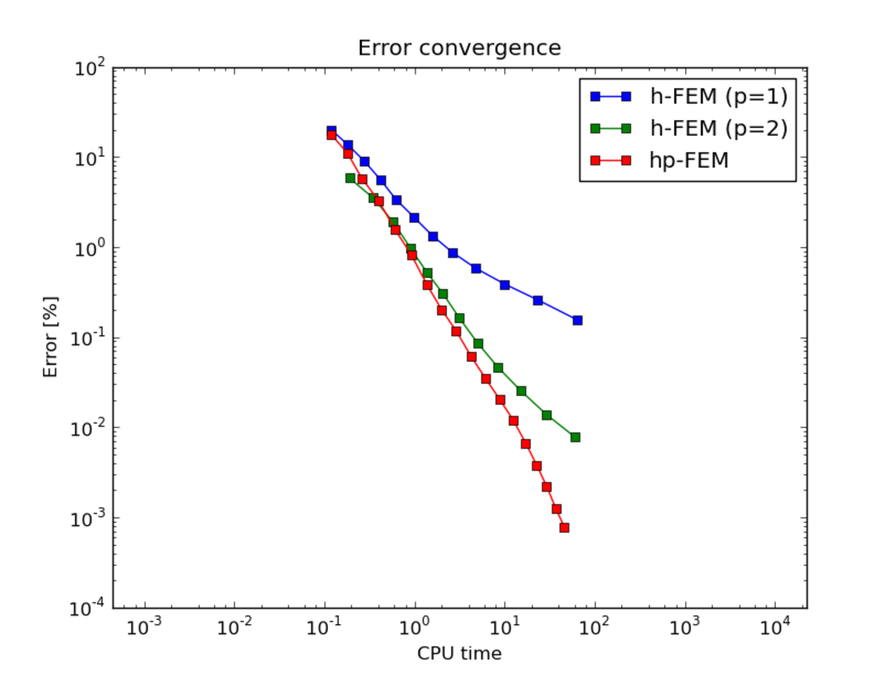
CPU time convergence graphs: