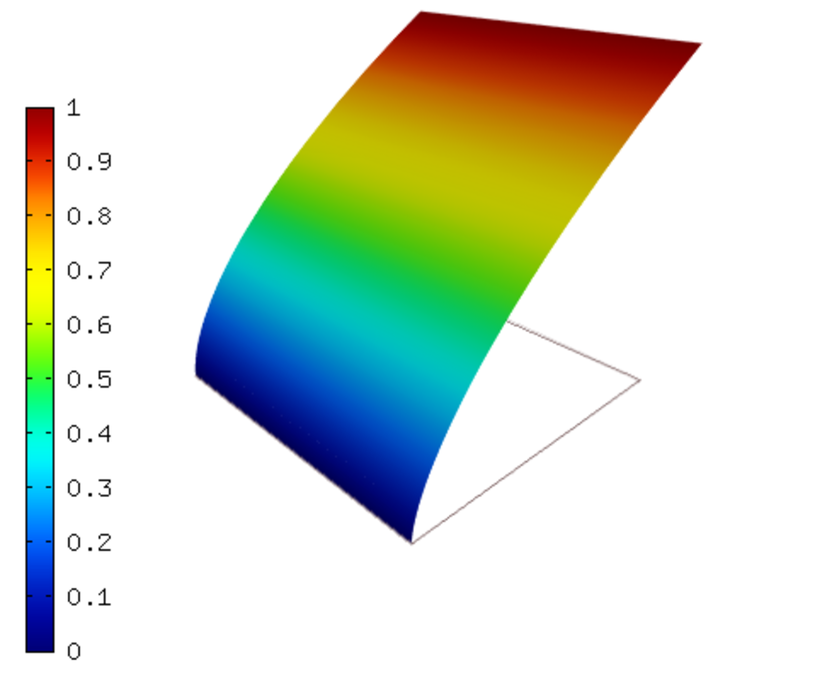
NIST-07 (Boundary Line Singularity)¶
Many papers on testing adaptive algorithms use a 1D example with a singularity of the form 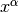 at the left endpoint of the domain. This can be extended to 2D by simply making the solution be
constant in
at the left endpoint of the domain. This can be extended to 2D by simply making the solution be
constant in 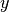 .
.
Model problem¶
Equation solved: Poisson equation
(1)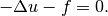
Domain of interest: Unit Square 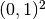
Boundary conditions: Dirichlet, given by exact solution.
Right-hand side¶
Obtained by inserting the exact solution into the equation.
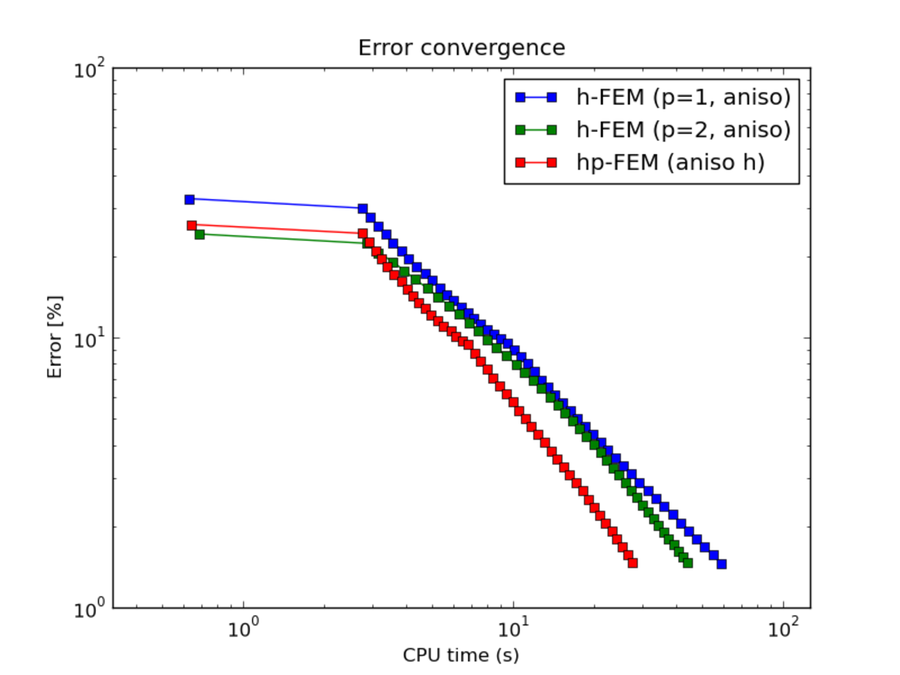
Comparison of h-FEM (p=1), h-FEM (p=2) and hp-FEM with anisotropic refinements¶
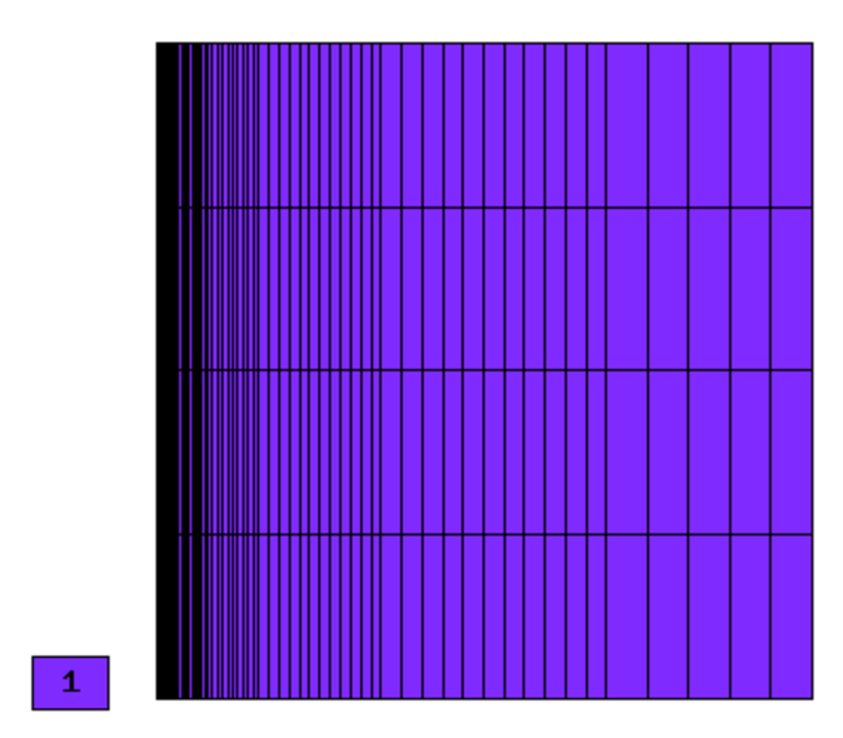
Final mesh (h-FEM, p=1, anisotropic refinements):
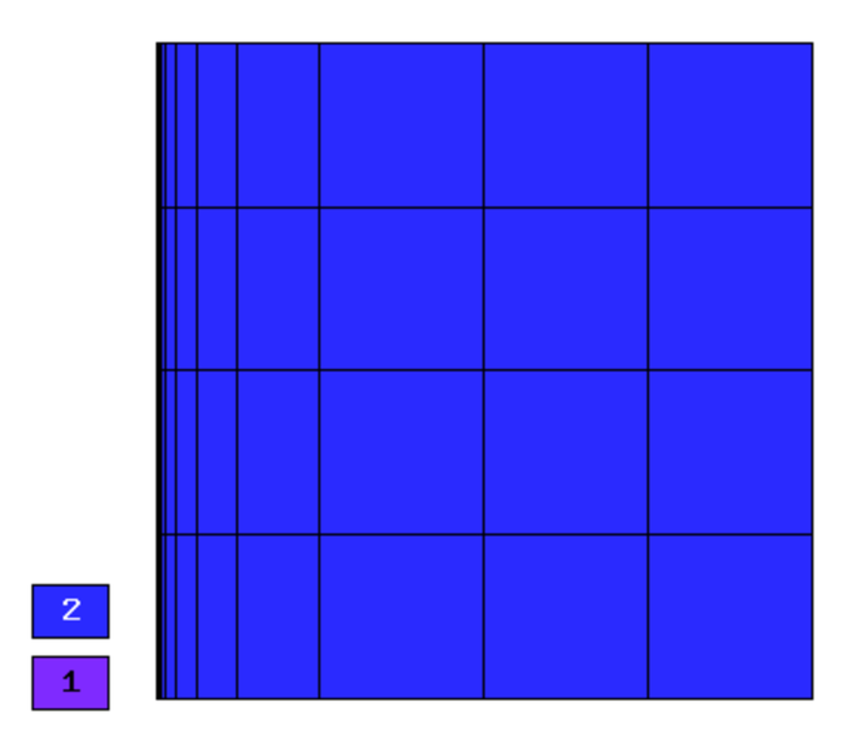
Final mesh (h-FEM, p=2, anisotropic refinements):
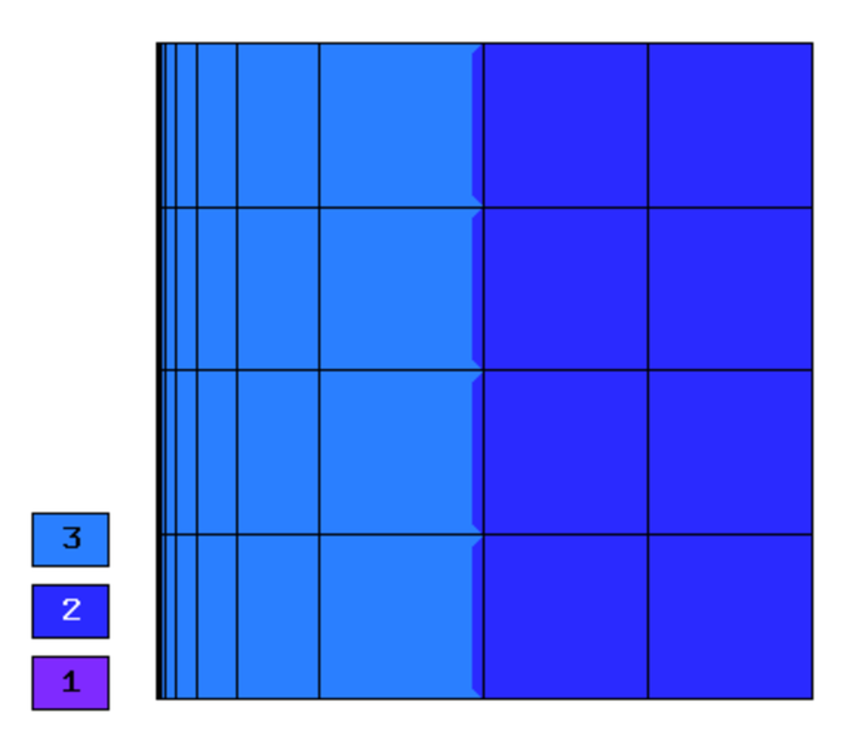
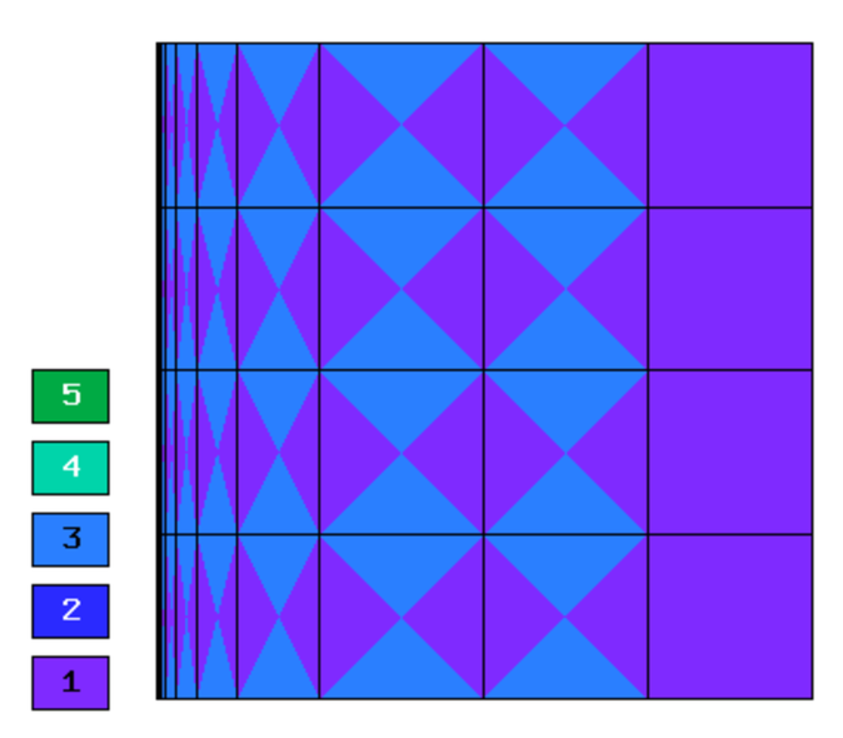
Final mesh (hp-FEM, h-anisotropic refinements):
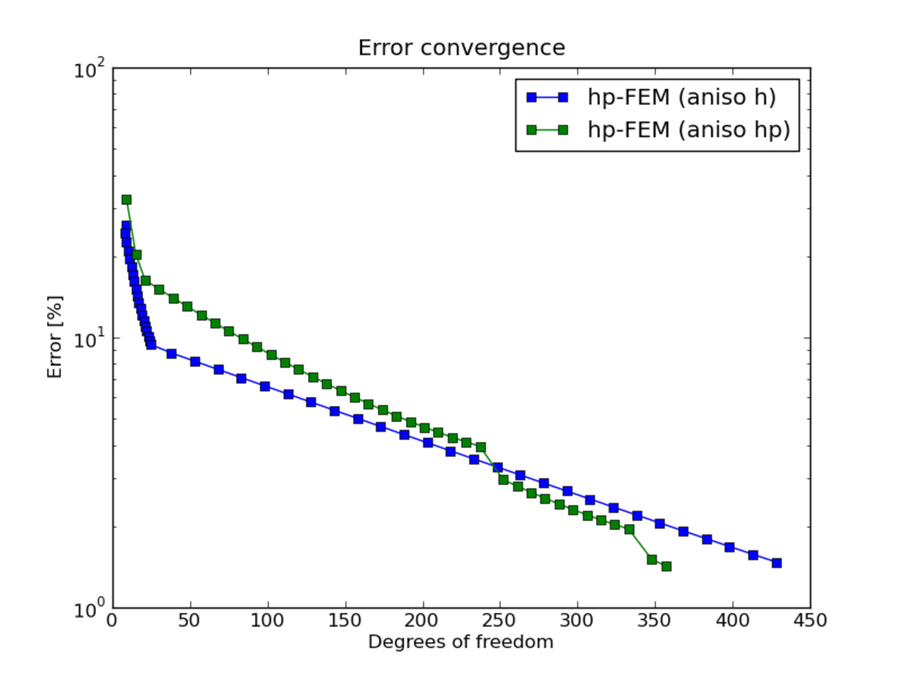
DOF convergence graphs:
CPU convergence graphs:
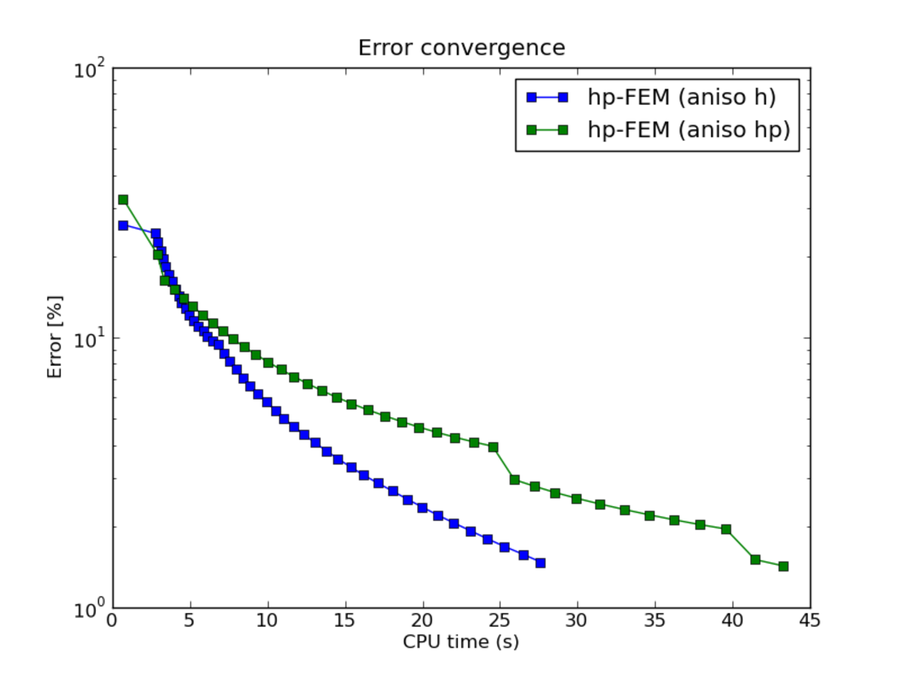
hp-FEM with h-aniso and hp-aniso refinements¶
Final mesh (hp-FEM, h-anisotropic refinements):
Final mesh (hp-FEM, hp-anisotropic refinements):
DOF convergence graphs:
CPU convergence graphs:
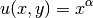
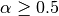 determines the strength of the singularity.
determines the strength of the singularity.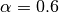 :
: